8i | 9i | 10g | 11g | 12c | 13c | 18c | 19c | 21c | 23c | Misc | PL/SQL | SQL | RAC | WebLogic | Linux
Multitenant : Hot Clone a Remote PDB or Non-CDB in Oracle Database 12c Release 2 (12.2)
In the initial release of Oracle Database 12c Release 1 (12.1.0.1) remote cloning of PDBs was listed as a feature, but it didn't work. The 12.1.0.2 patch fixed that, but also added the ability to create a PDB as a clone of a remote non-CDB database. The biggest problem with remote cloning was the prerequisite of placing the source PDB or non-CDB into read-only mode before initiating the cloning process. This made this feature useless for cloning production systems, as that level of down-time is typically unacceptable. Oracle Database 12c Release 2 (12.2) removes this prerequisite, which enables hot cloning of PDBs and non-CDBs for the first time.
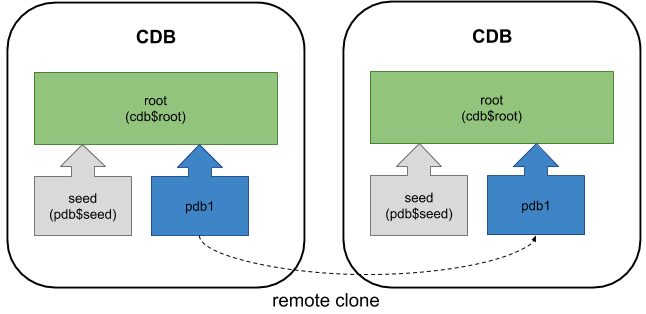
This article is an update of one written for a previous version, seen here. The previous article is still valid for Oracle 12.2, but it doesn't represent hot cloning.
Related articles.
- Multitenant : All Articles
- Multitenant : Local Undo Mode in Oracle Database 12c Release 2 (12.2)
- Multitenant : Hot Clone a Pluggable Database (PDB)
- Multitenant : YouTube Playlist
- Multitenant : Create and Configure a Pluggable Database (PDB) in Oracle Database 12c Release 1 (12.1)
Prerequisites
The prerequisites for cloning a remote PDB or non-CDB are very similar, so I will deal with them together.
In this context, the word "local" refers to the destination or target CDB that will house the cloned PDB. The word "remote" refers to the PDB or non-CDB that is the source of the clone.
- The user in the local database must have the
CREATE PLUGGABLE DATABASEprivilege in the root container. - The remote CDB must use local undo mode. Without this you must open the remote PDB or non-CDB in read-only mode.
- The remote database should be in archivelog mode. Without this you must open the remote PDB or non-CDB in read-only mode.
- The local database must have a database link to the remote database. If the remote database is a PDB, the database link can point to the remote CDB using a common user, the PDB or an application container using a local or common user.
- The user in the remote database that the database link connects to must have the
CREATE PLUGGABLE DATABASEprivilege. - The local and remote databases must have the same endianness.
- The local and remote databases must either have the same options installed, or the remote database must have a subset of those present on the local database.
- If the character set of the local CDB is AL32UTF8, the remote database can be any character set. If the local CDB does not use AL32UTF8, the character sets of the remote and local databases much match.
- If the remote database uses Transparent Data Encryption (TDE) the local CDB must be configured appropriately before attempting the clone. If not you will be left with a new PDB that will only open in restricted mode.
- Bug 19174942 is marked as fixed in 12.2. I can't confirm this, so just in case I'll leave this here, but it should no longer be the case. The default tablespaces for each common user in the remote CDB *must* exist in local CDB. If this is not true, create the missing tablespaces in the root container of the local PDB. If you don't do this your new PDB will only be able to open in restricted mode (Bug 19174942).
- When cloning from a non-CDB, both the the local and remote databases must using version 12.1.0.2 or higher.
In the examples below I have three databases running on the same virtual machine, but they could be running on separate physical or virtual servers.
- cdb1 : The local database that will eventually house the clones.
- db12c : The remote non-CDB.
- cdb3 : The remote CDB, used for cloning a remote PDB (pdb5).
Cloning a Remote PDB
Connect to the remote CDB and prepare the remote PDB for cloning.
export ORAENV_ASK=NO export ORACLE_SID=cdb3 . oraenv export ORAENV_ASK=YES sqlplus / as sysdba
Create a user in the remote database for use with the database link. In this case, we will use a common user in the remote CDB.
CREATE USER c##remote_clone_user IDENTIFIED BY remote_clone_user CONTAINER=ALL; GRANT CREATE SESSION, CREATE PLUGGABLE DATABASE TO c##remote_clone_user CONTAINER=ALL;
Check the remote CDB is in local undo mode and archivelog mode.
CONN / AS SYSDBA COLUMN property_name FORMAT A30 COLUMN property_value FORMAT A30 SELECT property_name, property_value FROM database_properties WHERE property_name = 'LOCAL_UNDO_ENABLED'; PROPERTY_NAME PROPERTY_VALUE ------------------------------ ------------------------------ LOCAL_UNDO_ENABLED TRUE SQL> SELECT log_mode FROM v$database; LOG_MODE ------------ ARCHIVELOG SQL>
Because the remote CDB is in local undo mode and archivelog mode, we don't need to turn the remote database into read-only mode.
Switch to the local server and create a "tnsnames.ora" entry pointing to the remote database for use in the USING clause of the database link.
CDB3=
(DESCRIPTION =
(ADDRESS = (PROTOCOL = TCP)(HOST = my-server.my-domain)(PORT = 1521))
(CONNECT_DATA =
(SERVER = DEDICATED)
(SERVICE_NAME = cdb3)
)
)
Connect to the local database to initiate the clone.
export ORAENV_ASK=NO export ORACLE_SID=cdb1 . oraenv export ORAENV_ASK=YES sqlplus / as sysdba
Create a database link in the local database, pointing to the remote database.
DROP DATABASE LINK clone_link; CREATE DATABASE LINK clone_link CONNECT TO c##remote_clone_user IDENTIFIED BY remote_clone_user USING 'cdb3'; -- Test link. DESC user_tables@clone_link
Create a new PDB in the local database by cloning the remote PDB. In this case we are using Oracle Managed Files (OMF), so we don't need to bother with FILE_NAME_CONVERT parameter for file name conversions.
CREATE PLUGGABLE DATABASE pdb5new FROM pdb5@clone_link; Pluggable database created. SQL>
We can see the new PDB has been created, but it is in the MOUNTED state.
COLUMN name FORMAT A30 SELECT name, open_mode FROM v$pdbs WHERE name = 'PDB5NEW'; NAME OPEN_MODE ------------------------------ ---------- PDB5NEW MOUNTED SQL>
The PDB is opened in read-write mode to complete the process.
ALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASE pdb5new OPEN; SELECT name, open_mode FROM v$pdbs WHERE name = 'PDB5NEW'; NAME OPEN_MODE ------------------------------ ---------- PDB5NEW READ WRITE SQL>
As with any PDB clone, check common users and the temporary tablespace is configured as expected.
Cloning a Remote Non-CDB
Connect to the remote database to prepare it for cloning.
export ORAENV_ASK=NO export ORACLE_SID=db12c . oraenv export ORAENV_ASK=YES sqlplus / as sysdba
Create a user in the remote database for use with the database link.
CREATE USER remote_clone_user IDENTIFIED BY remote_clone_user; GRANT CREATE SESSION, CREATE PLUGGABLE DATABASE TO remote_clone_user;
Check the remote non-CDB is archivelog mode.
SELECT log_mode FROM v$database; LOG_MODE ------------ ARCHIVELOG SQL>
In Oracle 12.1 we would have switched the remote database to read-only mode before continuing, but this is not necessary in Oracle 12.2 provided the source database is in archivelog mode.
Switch to the local server and create a "tnsnames.ora" entry pointing to the remote database for use in the USING clause of the database link.
DB12C =
(DESCRIPTION =
(ADDRESS_LIST =
(ADDRESS = (PROTOCOL = TCP)(HOST = my-server.my-domain)(PORT = 1521))
)
(CONNECT_DATA =
(SERVICE_NAME = db12c)
)
)
Connect to the local database to initiate the clone.
export ORAENV_ASK=NO export ORACLE_SID=cdb1 . oraenv export ORAENV_ASK=YES sqlplus / as sysdba
Create a database link in the local database, pointing to the remote database.
DROP DATABASE LINK clone_link; CREATE DATABASE LINK clone_link CONNECT TO remote_clone_user IDENTIFIED BY remote_clone_user USING 'db12c'; -- Test link. DESC user_tables@clone_link
Create a new PDB in the local database by cloning the remote non-CDB. In this case we are using Oracle Managed Files (OMF), so we don't need to bother with FILE_NAME_CONVERT parameter for file name conversions. Since there is no PDB to name, we use "NON$CDB" as the PDB name.
CREATE PLUGGABLE DATABASE db12cpdb FROM NON$CDB@clone_link; Pluggable database created. SQL>
We can see the new PDB has been created, but it is in the MOUNTED state.
COLUMN name FORMAT A30 SELECT name, open_mode FROM v$pdbs WHERE name = 'DB12CPDB'; NAME OPEN_MODE ------------------------------ ---------- DB12CPDB MOUNTED SQL>
Since this PDB was created as a clone of a non-CDB, before it can be opened we need to run the "$ORACLE_HOME/rdbms/admin/noncdb_to_pdb.sql" script to clean it up.
ALTER SESSION SET CONTAINER=db12cpdb; @$ORACLE_HOME/rdbms/admin/noncdb_to_pdb.sql
The PDB can now be opened in read-write mode.
ALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASE db12cpdb OPEN; SELECT name, open_mode FROM v$pdbs WHERE name = 'DB12CPDB'; NAME OPEN_MODE ------------------------------ ---------- DB12CPDB READ WRITE SQL>
As with any PDB clone, check common users and the temporary tablespace is configured as expected.
Appendix
The following DBCA commands are used to create and delete the CDB instances and PDBs used for these examples.
# Local container (cdb1). dbca -silent -createDatabase \ -templateName General_Purpose.dbc \ -gdbname cdb1 -sid cdb1 -responseFile NO_VALUE \ -characterSet AL32UTF8 \ -sysPassword SysPassword1 \ -systemPassword SysPassword1 \ -createAsContainerDatabase true \ -numberOfPDBs 1 \ -pdbName pdb1 \ -pdbAdminPassword SysPassword1 \ -databaseType MULTIPURPOSE \ -memoryMgmtType auto_sga \ -totalMemory 2048 \ -storageType FS \ -datafileDestination "/u02/oradata/" \ -redoLogFileSize 50 \ -initParams encrypt_new_tablespaces=DDL \ -emConfiguration NONE \ -ignorePreReqs # Remote container (cdb3) with PDB (pdb5). dbca -silent -createDatabase \ -templateName General_Purpose.dbc \ -gdbname cdb3 -sid cdb3 -responseFile NO_VALUE \ -characterSet AL32UTF8 \ -sysPassword SysPassword1 \ -systemPassword SysPassword1 \ -createAsContainerDatabase true \ -numberOfPDBs 1 \ -pdbName pdb5 \ -pdbAdminPassword SysPassword1 \ -databaseType MULTIPURPOSE \ -memoryMgmtType auto_sga \ -totalMemory 2048 \ -storageType FS \ -datafileDestination "/u02/oradata/" \ -redoLogFileSize 50 \ -initParams encrypt_new_tablespaces=DDL \ -emConfiguration NONE \ -ignorePreReqs # Non-CDB instance (db12c). dbca -silent -createDatabase \ -templateName General_Purpose.dbc \ -gdbname db12c -sid db12c -responseFile NO_VALUE \ -characterSet AL32UTF8 \ -sysPassword SysPassword1 \ -systemPassword SysPassword1 \ -createAsContainerDatabase false \ -databaseType MULTIPURPOSE \ -memoryMgmtType auto_sga \ -totalMemory 2048 \ -storageType FS \ -datafileDestination "/u02/oradata/" \ -redoLogFileSize 50 \ -initParams encrypt_new_tablespaces=DDL \ -emConfiguration NONE \ -ignorePreReqs # Delete the instances. #dbca -silent -deleteDatabase -sourceDB cdb1 -sysDBAUserName sys -sysDBAPassword SysPassword1 dbca -silent -deleteDatabase -sourceDB cdb3 -sysDBAUserName sys -sysDBAPassword SysPassword1 dbca -silent -deleteDatabase -sourceDB db12c -sysDBAUserName sys -sysDBAPassword SysPassword1
As explained earlier, in all cases Oracle Managed Files (OMF) was used so no file name conversions were needed. Also, the source databases were switched to archivelog mode.
export ORAENV_ASK=NO export ORACLE_SID=cdb3 . oraenv export ORAENV_ASK=YES sqlplus / as sysdba <<EOF ALTER SYSTEM SET db_create_file_dest = '/u02/oradata'; SHUTDOWN IMMEDIATE; STARTUP MOUNT; ALTER DATABASE ARCHIVELOG; ALTER DATABASE OPEN; ALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASE pdb5 OPEN; ALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASE pdb5 SAVE STATE; EXIT; EOF
For more information see:
- Multitenant : All Articles
- Multitenant : Local Undo Mode in Oracle Database 12c Release 2 (12.2)
- Cloning a Remote PDB or Non-CDB
- Multitenant : Hot Clone a Pluggable Database (PDB)
- Multitenant : YouTube Playlist
- Multitenant : Create and Configure a Pluggable Database (PDB) in Oracle Database 12c Release 1 (12.1)
Hope this helps. Regards Tim...