8i | 9i | 10g | 11g | 12c | 13c | 18c | 19c | 21c | 23ai | Misc | PL/SQL | SQL | RAC | WebLogic | Linux
Hybrid Partitioned Tables in Oracle Database 19c
This article shows how to combine internal and external partitions into a single Hybrid Partitioned Table in Oracle Database 19c.
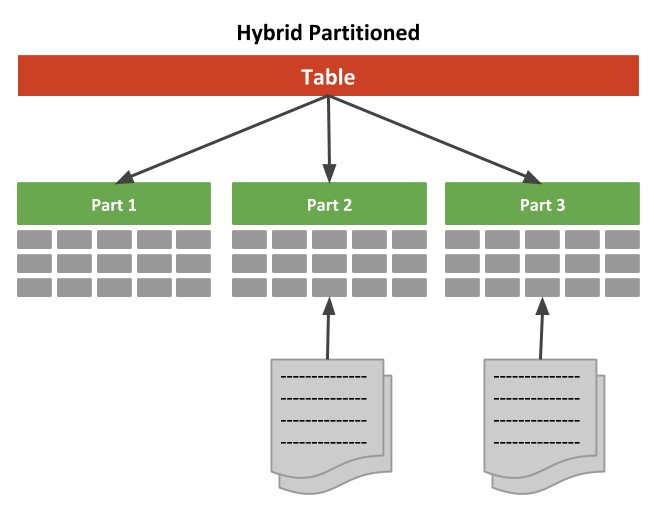
Hybrid partitioned tables support the following external table types for external partitions.
ORACLE_DATAPUMPORACLE_LOADERORACLE_HDFSORACLE_HIVE
In this article we'll focus on the ORACLE_LOADER and ORACLE_DATAPUMP examples.
- Setup
- Create Hybrid Partitioned Table (ORACLE_LOADER)
- Create Hybrid Partitioned Table (ORACLE_DATAPUMP)
- Add/Drop Partitions
- Restrictions
Related articles.
- Hybrid Partitioned Table Enhancements in Oracle Database 23ai
- Hybrid Partitioned Tables in Oracle Database 19c
- Partitioning : All Articles
- External Tables : All Articles
- Data Pump (expdp, impdp) : All Articles
Setup
Connect to a privileged user and create a new test user called TESTUSER1.
CONN sys/SysPassword1@//localhost:1521/pdb1 AS SYSDBA --DROP USER testuser1 CASCADE; CREATE USER testuser1 IDENTIFIED BY testuser1 QUOTA UNLIMITED ON users; GRANT CREATE SESSION, CREATE TABLE TO testuser1;
Create two new directory objects, making sure TESTUSER1 has READ, WRITE and EXECUTE permissions on them.
CREATE OR REPLACE DIRECTORY TMP_DIR1 AS '/tmp/'; GRANT READ, WRITE, EXECUTE ON DIRECTORY TMP_DIR1 TO testuser1; CREATE OR REPLACE DIRECTORY TMP_DIR2 AS '/tmp/'; GRANT READ, WRITE, EXECUTE ON DIRECTORY TMP_DIR2 TO testuser1;
All other actions will be performed from TESTUSER1.
CONN testuser1/testuser1@//localhost:1521/pdb1
Create Hybrid Partitioned Table (ORACLE_LOADER)
Generate some flat files with dummy data for use with external table partitions.
SET MARKUP CSV ON QUOTE ON
SET TRIMSPOOL ON LINESIZE 1000 FEEDBACK OFF PAGESIZE 0
SPOOL /tmp/gbr1.txt
SELECT 'GBR',
object_id,
owner,
object_name
FROM all_objects
WHERE object_id <= 3999
AND rownum <= 1000;
SPOOL OFF
SPOOL /tmp/gbr2.txt
SELECT 'GBR',
object_id,
owner,
object_name
FROM all_objects
WHERE object_id BETWEEN 4000 AND 5999
AND rownum <= 1000;
SPOOL OFF
SPOOL /tmp/ire1.txt
SELECT 'IRE',
object_id,
owner,
object_name
FROM all_objects
WHERE object_id <= 3999
AND rownum <= 1000;
SPOOL OFF
SPOOL /tmp/ire2.txt
SELECT 'IRE',
object_id,
owner,
object_name
FROM all_objects
WHERE object_id BETWEEN 4000 AND 5999
AND rownum <= 1000;
SPOOL OFF
SET MARKUP CSV OFF
SET TRIMSPOOL ON LINESIZE 1000 FEEDBACK ON PAGESIZE 14
The following example creates a hybrid partitioned table. It uses list partitioning, with a single internal partition for USA data, and two external partitions for GBR and IRE data respectively.
--DROP TABLE test_ol_hybrid_part_tab PURGE;
CREATE TABLE test_ol_hybrid_part_tab (
country_code VARCHAR2(3) NOT NULL,
object_id NUMBER NOT NULL,
owner VARCHAR2(128) NOT NULL,
object_name VARCHAR2(128) NOT NULL
)
EXTERNAL PARTITION ATTRIBUTES (
TYPE ORACLE_LOADER
DEFAULT DIRECTORY tmp_dir1
ACCESS PARAMETERS (
FIELDS CSV WITH EMBEDDED TERMINATED BY ',' OPTIONALLY ENCLOSED BY '"'
MISSING FIELD VALUES ARE NULL
(country_code, object_id, owner, object_name)
)
REJECT LIMIT UNLIMITED
)
PARTITION BY LIST (country_code) (
PARTITION usa VALUES ('USA'),
PARTITION gbr VALUES ('GBR') EXTERNAL
LOCATION ('gbr1.txt', 'gbr2.txt'),
PARTITION ire VALUES ('IRE') EXTERNAL
DEFAULT DIRECTORY tmp_dir2 LOCATION ('ire1.txt', 'ire2.txt')
);
The EXTERNAL PARTITION ATTRIBUTES clause defines the table-level external table parameters. For external partitions, the EXTERNAL clause is used to define partition-level attributes, such as file locations and non-default directory objects.
The HYBRID column in the CDB|DBA|ALL|USER}_TABLES views show this is a hybrid table.
COLUMN table_name FORMAT A30 COLUMN hybrid FORMAT A6 SELECT table_name, hybrid FROM user_tables; TABLE_NAME HYBRID ------------------------------ ------ TEST_OL_HYBRID_PART_TAB YES SQL>
We only have data in the external partitions at the moment.
COLUMN country_code FORMAT A12 SELECT country_code, COUNT(*) as amount FROM test_ol_hybrid_part_tab GROUP BY country_code ORDER BY country_code; COUNTRY_CODE AMOUNT ------------ ---------- GBR 2000 IRE 2000 SQL>
We can perform DML on the internal partition as normal.
INSERT INTO test_ol_hybrid_part_tab
SELECT 'USA',
object_id,
owner,
object_name
FROM all_objects
WHERE rownum <= 2000;
COMMIT;
COLUMN country_code FORMAT A12
SELECT country_code, COUNT(*) as amount
FROM test_ol_hybrid_part_tab
GROUP BY country_code
ORDER BY country_code;
COUNTRY_CODE AMOUNT
------------ ----------
GBR 2000
IRE 2000
USA 2000
SQL>
As you might expect, trying to insert into the external partitions results in an error.
INSERT INTO test_ol_hybrid_part_tab VALUES ('GBR', 9999, 'X', 'X');
*
ERROR at line 1:
ORA-14466: Data in a read-only partition or subpartition cannot be modified.
SQL>
The full list of supported operations can be found in the Hybrid Partitioned Tables document.
Create Hybrid Partitioned Table (ORACLE_DATAPUMP)
We create a dump file called "bgr_xt.dmp" containing BGR data. Creating the external table generates the Data Pump dump file. When we drop the table the dump file remains on the database file system, so we can use it for our test.
CREATE TABLE bgr_xt
ORGANIZATION EXTERNAL
(
TYPE ORACLE_DATAPUMP
DEFAULT DIRECTORY tmp_dir1
LOCATION ('bgr_xt.dmp')
) AS
SELECT 'BGR' AS country_code,
object_id,
owner,
object_name
FROM all_objects
WHERE rownum <= 2000;
DROP TABLE bgr_xt;
The following example creates a hybrid partitioned table. It uses list partitioning, with a single internal partition for USA data, and a data pump external partitions for BGR data.
--DROP TABLE test_dp_hybrid_part_tab PURGE;
CREATE TABLE test_dp_hybrid_part_tab (
country_code VARCHAR2(3) NOT NULL,
object_id NUMBER NOT NULL,
owner VARCHAR2(128) NOT NULL,
object_name VARCHAR2(128) NOT NULL
)
EXTERNAL PARTITION ATTRIBUTES (
TYPE ORACLE_DATAPUMP
DEFAULT DIRECTORY tmp_dir1
)
PARTITION BY LIST (country_code) (
PARTITION usa VALUES ('USA'),
PARTITION bgr VALUES ('BGR') EXTERNAL
LOCATION ('bgr_xt.dmp')
);
The EXTERNAL PARTITION ATTRIBUTES clause defines the table-level Data Pump external table parameters. For external partitions, the EXTERNAL clause is used to define partition-level attributes, such as file locations and non-default directory objects.
The HYBRID column in the CDB|DBA|ALL|USER}_TABLES views show this is a hybrid table.
COLUMN table_name FORMAT A30 COLUMN hybrid FORMAT A6 SELECT table_name, hybrid FROM user_tables; TEST_OL_HYBRID_PART_TAB YES TEST_DP_HYBRID_PART_TAB YES SQL>
We only have data in the external partitions at the moment.
COLUMN country_code FORMAT A12 SELECT country_code, COUNT(*) as amount FROM test_dp_hybrid_part_tab GROUP BY country_code ORDER BY country_code; COUNTRY_CODE AMOUNT ------------ ---------- BGR 2000 SQL>
We can perform DML on the internal partition as normal.
INSERT INTO test_dp_hybrid_part_tab
SELECT 'USA',
object_id,
owner,
object_name
FROM all_objects
WHERE rownum <= 2000;
COMMIT;
COLUMN country_code FORMAT A12
SELECT country_code, COUNT(*) as amount
FROM test_dp_hybrid_part_tab
GROUP BY country_code
ORDER BY country_code;
COUNTRY_CODE AMOUNT
------------ ----------
BGR 2000
USA 2000
SQL>
As you might expect, trying to insert into the external partitions results in an error.
INSERT INTO test_dp_hybrid_part_tab VALUES ('GBR', 9999, 'X', 'X');
*
ERROR at line 1:
ORA-14466: Data in a read-only partition or subpartition cannot be modified.
SQL>
The full list of supported operations can be found in the Hybrid Partitioned Tables document.
Add/Drop Partitions
We can add and drop partitions in a normal manner.
We drop the partition for the IRE data from the TEST_OL_HYBRID_PART_TAB table.
ALTER TABLE test_ol_hybrid_part_tab DROP PARTITION ire; COLUMN country_code FORMAT A12 SELECT country_code, COUNT(*) as amount FROM test_ol_hybrid_part_tab GROUP BY country_code ORDER BY country_code; COUNTRY_CODE AMOUNT ------------ ---------- GBR 2000 USA 2000 SQL>
We add back the partition for the IRE data.
ALTER TABLE test_ol_hybrid_part_tab ADD PARTITION ire VALUES ('IRE') EXTERNAL
DEFAULT DIRECTORY tmp_dir2 LOCATION ('ire1.txt', 'ire2.txt');
COLUMN country_code FORMAT A12
SELECT country_code, COUNT(*) as amount
FROM test_ol_hybrid_part_tab
GROUP BY country_code
ORDER BY country_code;
COUNTRY_CODE AMOUNT
------------ ----------
GBR 2000
IRE 2000
USA 2000
SQL>
We drop the partition for the BGR data from the TEST_DP_HYBRID_PART_TAB table.
ALTER TABLE test_dp_hybrid_part_tab DROP PARTITION bgr; COLUMN country_code FORMAT A12 SELECT country_code, COUNT(*) as amount FROM test_dp_hybrid_part_tab GROUP BY country_code ORDER BY country_code; COUNTRY_CODE AMOUNT ------------ ---------- USA 2000 SQL>
We add back the partition for the BGR data.
ALTER TABLE test_dp_hybrid_part_tab ADD PARTITION bgr VALUES ('BGR') EXTERNAL
DEFAULT DIRECTORY tmp_dir2 LOCATION ('bgr_xt.dmp');
COLUMN country_code FORMAT A12
SELECT country_code, COUNT(*) as amount
FROM test_dp_hybrid_part_tab
GROUP BY country_code
ORDER BY country_code;
COUNTRY_CODE AMOUNT
------------ ----------
BGR 2000
USA 2000
SQL>
The operations on the internal partitions are as you would expect to regular partitioned tables. The full list of supported operations can be found in the Hybrid Partitioned Tables document.
Restrictions
The standout restrictions are as follows.
- You can only use
RANGEorLISTpartitioning. - There is no support for
REFERENCEandSYSTEMpartitioning.
Most of the other restrictions are what you would expect for the various types of partitions.
The full list of restrictions can be found in the Hybrid Partitioned Tables document.
For more information see:
- Hybrid Partitioned Tables
- Managing Hybrid Partitioned Tables
- Hybrid Partitioned Table Enhancements in Oracle Database 23ai
- Hybrid Partitioned Tables in Oracle Database 19c
- Partitioning : All Articles
- External Tables : Querying Data From Flat Files in Oracle
- Data Pump : External Tables (Unloading/Loading Data Using External Tables)
- ORACLE_DATAPUMP Access Driver Enhancements
- ORACLE_LOADER Access Driver Enhancements
- External Tables : All Articles
- Data Pump (expdp, impdp) : All Articles
Hope this helps. Regards Tim...